资讯专栏INFORMATION COLUMN

小编写这篇文章的一个主要目的,主要是来给大家去做一个介绍,介绍的内容主要是关于Python的一些知识,其中的内容包含有xpath,JsonPath,bs4等一些知识,主要是去介绍他们的一些基本使用方法,具体的内容,下面就给大家详细解答下。
1.xpath
1.1 xpath使用
google提前安装xpath插件,按ctrl+shift+x出现小黑框
安装lxml库pip install lxml‐i https://pypi.douban.com/simple
导入lxml.etreefrom lxml import etree
etree.parse()解析本地文件html_tree=etree.parse('XX.html')
etree.HTML()服务器响应文件html_tree=etree.HTML(response.read().decode('utf‐8')
.html_tree.xpath(xpath路径)
1.2 xpath基本语法
1.路径查询
查找所有子孙节点,不考虑层级关系
找直接子节点
2.谓词查询
//div[id] //div[id="maincontent"]
3.属性查询
//class
4.模糊查询
//div[contains(id,"he")] //div[starts‐with(id,"he")]
5.内容查询
//div/h1/text()
6.逻辑运算
//div[id="head"and] //title|//price
1.3示例
xpath.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li id="l1"class="class1">北京</li>
<li id="l2"class="class2">上海</li>
<li id="d1">广州</li>
<li>深圳</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
from lxml import etree
#xpath解析
#本地文件:etree.parse
#服务器相应的数据response.read().decode('utf-8')etree.HTML()
tree=etree.parse('xpath.html')
#查找url下边的li
li_list=tree.xpath('//body/ul/li')
print(len(li_list))#4
#获取标签中的内容
li_list=tree.xpath('//body/ul/li/text()')
print(li_list)#['北京','上海','广州','深圳']
#获取带id属性的li
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id]')
print(len(li_list))#3
#获取id为l1的标签内容
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l1"]/text()')
print(li_list)#['北京']
#获取id为l1的class属性值
c1=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l1"]/class')
print(c1)#['class1']
#获取id中包含l的标签
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[contains(id,"l")]/text()')
print(li_list)#['北京','上海']
#获取id以d开头的标签
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[starts-with(id,"d")]/text()')
print(li_list)#['广州']
#获取id为l2并且class为class2的标签
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l2"and]/text()')
print(li_list)#['上海']
#获取id为l2或id为d1的标签
li_list=tree.xpath('//ul/li[id="l2"]/text()|//ul/li[id="d1"]/text()')
print(li_list)#['上海','广州']1.4爬取百度搜索按钮的value
import urllib.request
from lxml import etree
url='http://www.baidu.com'
headers={
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0(Windows NT 10.0;Win64;x64)AppleWebKit/537.36(KHTML,like Gecko)Chrome/103.0.0.0 Safari/537.36'
}
request=urllib.request.Request(url=url,headers=headers)
response=urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content=response.read().decode('utf-8')
tree=etree.HTML(content)
value=tree.xpath('//input[id="su"]/value')
print(value)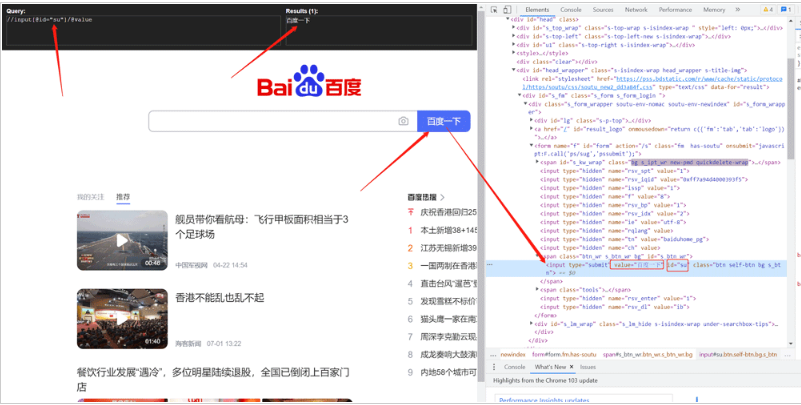
1.5爬取站长素材的图片
#需求下载的前十页的图片
#https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian.html 1
#https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian_page.html
import urllib.request
from lxml import etree
def create_request(page):
if(page==1):
url='https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian.html'
else:
url='https://sc.chinaz.com/tupian/qinglvtupian_'+str(page)+'.html'
headers={
'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0(Windows NT 10.0;Win64;x64)AppleWebKit/537.36(KHTML,like Gecko)Chrome/92.0.4515.159 Safari/537.36',
}
request=urllib.request.Request(url=url,headers=headers)
return request
def get_content(request):
response=urllib.request.urlopen(request)
content=response.read().decode('utf-8')
return content
def down_load(content):
#下载图片
#urllib.request.urlretrieve('图片地址','文件的名字')
tree=etree.HTML(content)
name_list=tree.xpath('//div[id="container"]//a/img/alt')
#一般设计图片的网站都会进行懒加载
src_list=tree.xpath('//div[id="container"]//a/img/src2')
print(src_list)
for i in range(len(name_list)):
name=name_list<i>
src=src_list<i>
url='https:'+src
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url=url,filename='./loveImg/'+name+'.jpg')
if __name__=='__main__':
start_page=int(input('请输入起始页码'))
end_page=int(input('请输入结束页码'))
for page in range(start_page,end_page+1):
#(1)请求对象的定制
request=create_request(page)
#(2)获取网页的源码
content=get_content(request)
#(3)下载
down_load(content)2.JsonPath
2.1 pip安装
pip install jsonpath
2.2 jsonpath的使用
obj=json.load(open('json文件','r',encoding='utf‐8'))
ret=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'jsonpath语法')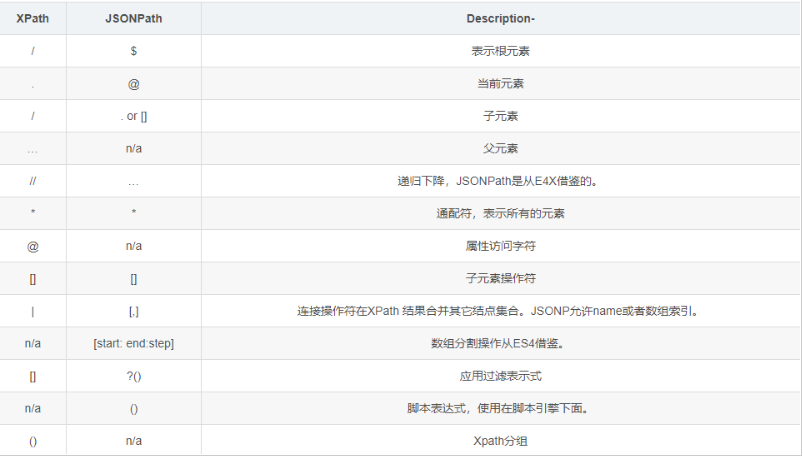
JSONPath语法元素和对应XPath元素的对比:
示例:
jsonpath.json
{"store":{
"book":[
{"category":"修真",
"author":"六道",
"title":"坏蛋是怎样练成的",
"price":8.95
},
{"category":"修真",
"author":"天蚕土豆",
"title":"斗破苍穹",
"price":12.99
},
{"category":"修真",
"author":"唐家三少",
"title":"斗罗大陆",
"isbn":"0-553-21311-3",
"price":8.99
},
{"category":"修真",
"author":"南派三叔",
"title":"星辰变",
"isbn":"0-395-19395-8",
"price":22.99
}
],
"bicycle":{
"author":"老马",
"color":"黑色",
"price":19.95
}
}
}
import json
import jsonpath
obj=json.load(open('jsonpath.json','r',encoding='utf-8'))
#书店所有书的作者
author_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$.store.book[*].author')
print(author_list)#['六道','天蚕土豆','唐家三少','南派三叔']
#所有的作者
author_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..author')
print(author_list)#['六道','天蚕土豆','唐家三少','南派三叔','老马']
#store下面的所有的元素
tag_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$.store.*')
print(
tag_list)#[[{'category':'修真','author':'六道','title':'坏蛋是怎样练成的','price':8.95},{'category':'修真','author':'天蚕土豆','title':'斗破苍穹','price':12.99},{'category':'修真','author':'唐家三少','title':'斗罗大陆','isbn':'0-553-21311-3','price':8.99},{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰变','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}],{'author':'老马','color':'黑色','price':19.95}]
#store里面所有东西的price
price_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$.store..price')
print(price_list)#[8.95,12.99,8.99,22.99,19.95]
#第三个书
book=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[2]')
print(book)#[{'category':'修真','author':'唐家三少','title':'斗罗大陆','isbn':'0-553-21311-3','price':8.99}]
#最后一本书
book=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[(.length-1)]')
print(book)#[{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰变','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}]
#前面的两本书
book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[0,1]')
#book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[:2]')
print(
book_list)#[{'category':'修真','author':'六道','title':'坏蛋是怎样练成的','price':8.95},{'category':'修真','author':'天蚕土豆','title':'斗破苍穹','price':12.99}]
#条件过滤需要在()的前面添加一个?
#过滤出所有的包含isbn的书。
book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[?(.isbn)]')
print(
book_list)#[{'category':'修真','author':'唐家三少','title':'斗罗大陆','isbn':'0-553-21311-3','price':8.99},{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰变','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}]
#哪本书超过了10块钱
book_list=jsonpath.jsonpath(obj,'$..book[?(.price>10)]')
print(
book_list)#[{'category':'修真','author':'天蚕土豆','title':'斗破苍穹','price':12.99},{'category':'修真','author':'南派三叔','title':'星辰变','isbn':'0-395-19395-8','price':22.99}]3.BeautifulSoup
3.1基本简介
1.安装
pip install bs4
2.导入
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
3.创建对象
服务器响应的文件生成对象soup=BeautifulSoup(response.read().decode(),'lxml')
本地文件生成对象soup=BeautifulSoup(open('1.html'),'lxml')
注意:默认打开文件的编码格式gbk所以需要指定打开编码格式utf-8
3.2安装以及创建
1.根据标签名查找节点
soup.a【注】只能找到第一个a soup.a.name soup.a.attrs
2.函数
(1).find(返回一个对象)
find('a'):只找到第一个a标签
find('a',title='名字')
find('a',class_='名字')
(2).find_all(返回一个列表)
find_all('a')查找到所有的a
find_all(['a','span'])返回所有的a和span
find_all('a',limit=2)只找前两个a
(3).select(根据选择器得到节点对象)【推荐】
1.element
eg:p
2..class
eg:.firstname
3.#id
eg:#firstname
4.属性选择器
[attribute]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class]')
[attribute=value]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class="hengheng1"]')
5.层级选择器
element element
div p
element>element
div>p
element,element
div,p
eg:soup=soup.select('a,span')
3.3节点定位
1.根据标签名查找节点
soup.a【注】只能找到第一个a
soup.a.name
soup.a.attrs
2.函数
(1).find(返回一个对象)
find('a'):只找到第一个a标签
find('a',title='名字')
find('a',class_='名字')
(2).find_all(返回一个列表)
find_all('a')查找到所有的a
find_all(['a','span'])返回所有的a和span
find_all('a',limit=2)只找前两个a
(3).select(根据选择器得到节点对象)【推荐】
1.element
eg:p
2..class
eg:.firstname
3.#id
eg:#firstname
4.属性选择器
[attribute]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class]')
[attribute=value]
eg:li=soup.select('li[class="hengheng1"]')
5.层级选择器
element element
div p
element>element
div>p
element,element
div,p
eg:soup=soup.select('a,span')
3.5节点信息
(1).获取节点内容:适用于标签中嵌套标签的结构
obj.string
obj.get_text()【推荐】
(2).节点的属性
tag.name获取标签名
eg:tag=find('li)
print(tag.name)
tag.attrs将属性值作为一个字典返回
(3).获取节点属性
obj.attrs.get('title')【常用】
obj.get('title')
obj['title']
(1).获取节点内容:适用于标签中嵌套标签的结构
obj.string
obj.get_text()【推荐】
(2).节点的属性
tag.name获取标签名
eg:tag=find('li)
print(tag.name)
tag.attrs将属性值作为一个字典返回
(3).获取节点属性
obj.attrs.get('title')【常用】
obj.get('title')
obj['title']
3.6使用示例
bs4.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li id="l1">张三</li>
<li id="l2">李四</li>
<li>王五</li>
<a href=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow""class="a1">google</a>
<span>嘿嘿嘿</span>
</ul>
</div>
<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>
<div id="d1">
<span>
哈哈哈
</span>
</div>
<p id="p1"class="p1">呵呵呵</p>
</body>
</html>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#通过解析本地文件来将bs4的基础语法进行讲解
#默认打开的文件的编码格式是gbk所以在打开文件的时候需要指定编码
soup=BeautifulSoup(open('bs4.html',encoding='utf-8'),'lxml')
#根据标签名查找节点
#找到的是第一个符合条件的数据
print(soup.a)#<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>
#获取标签的属性和属性值
print(soup.a.attrs)#{'href':'','id':'','class':['a1']}
#bs4的一些函数
#(1)find
#返回的是第一个符合条件的数据
print(soup.find('a'))#<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>
#根据title的值来找到对应的标签对象
print(soup.find('a',title="a2"))#<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>
#根据class的值来找到对应的标签对象注意的是class需要添加下划线
print(soup.find('a',class_="a1"))#<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>
#(2)find_all返回的是一个列表并且返回了所有的a标签
print(soup.find_all('a'))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>]
#如果想获取的是多个标签的数据那么需要在find_all的参数中添加的是列表的数据
print(soup.find_all(['a','span']))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<span>嘿嘿嘿</span>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百</a><spa哈</span>]
#limit的作用是查找前几个数据
print(soup.find_all('li',limit=2))#[<li id="l1">张三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>]
#(3)select(推荐)
#select方法返回的是一个列表并且会返回多个数据
print(soup.select('a'))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>]
#可以通过.代表class我们把这种操作叫做类选择器
print(soup.select('.a1'))#[<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>]
print(soup.select('#l1'))#[<li id="l1">张三</li>]
#属性选择器---通过属性来寻找对应的标签
#查找到li标签中有id的标签
print(soup.select('li[id]'))#[<li id="l1">张三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>]
#查找到li标签中id为l2的标签
print(soup.select('li[id="l2"]'))#[<li id="l2">李四</li>]
#层级选择器
#后代选择器
#找到的是div下面的li
print(soup.select('div li'))#[<li id="l1">张三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>,<li>王五</li>]
#子代选择器
#某标签的第一级子标签
#注意:很多的计算机编程语言中如果不加空格不会输出内容但是在bs4中不会报错会显示内容
print(soup.select('div>ul>li'))#[<li id="l1">张三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>,<li>王五</li>]
#找到a标签和li标签的所有的对象
print(soup.select(
'a,li'))#[<li id="l1">张三</li>,<li id="l2">李四</li>,<li>王五</li>,<ahref=""id="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"">google</a>,<a href=""title="rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"rel="external nofollow"a2">百度</a>]
#节点信息
#获取节点内容
obj=soup.select('#d1')[0]
#如果标签对象中只有内容那么string和get_text()都可以使用
#如果标签对象中除了内容还有标签那么string就获取不到数据而get_text()是可以获取数据
#我们一般情况下推荐使用get_text()
print(obj.string)#None
print(obj.get_text())#哈哈哈
#节点的属性
obj=soup.select('#p1')[0]
#name是标签的名字
print(obj.name)#p
#将属性值左右一个字典返回
print(obj.attrs)#{'id':'p1','class':['p1']}
#获取节点的属性
obj=soup.select('#p1')[0]
#
print(obj.attrs.get('class'))#['p1']
print(obj.get('class'))#['p1']
print(obj['class'])#['p1']
3.7解析星巴克产品名称
import urllib.request
url='https://www.starbucks.com.cn/menu/'
response=urllib.request.urlopen(url)
content=response.read().decode('utf-8')
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(content,'lxml')
#//ul[class="grid padded-3 product"]//strong/text()
#一般先用xpath方式通过google插件写好解析的表达式
name_list=soup.select('ul[class="grid padded-3 product"]strong')
for name in name_list:
print(name.get_text())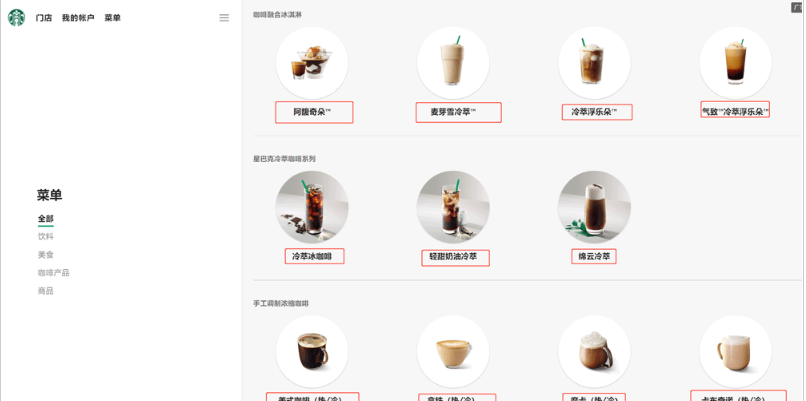
综上所述,这篇文章就给大家介绍到这里了,希望可以为大家带来更多帮助。
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载,若此文章存在违规行为,您可以联系管理员删除。
转载请注明本文地址:https://www.ucloud.cn/yun/128400.html
摘要:并不是所有爬虫都遵守,一般只有大型搜索引擎爬虫才会遵守。的端口号为的端口号为工作原理网络爬虫抓取过程可以理解为模拟浏览器操作的过程。表示服务器成功接收请求并已完成整个处理过程。 爬虫概念 数据获取的方式: 企业生产的用户数据:大型互联网公司有海量用户,所以他们积累数据有天然优势。有数据意识的中小型企业,也开始积累的数据。 数据管理咨询公司 政府/机构提供的公开数据 第三方数据平台购买...
摘要:主要用于选择器抽象类,实现类前面说的两个接口,主要用于选择器继承。多个选择的情形,每个选择器各自独立选择,将所有结果合并。抽象类,定义了一些模板方法。这部分源码就不做分析了。这里需要提到的一点是返回的不支持选择,返回的对象支持选择。 1、Selector部分:接口:Selector:定义了根据字符串选择单个元素和选择多个元素的方法。ElementSelector:定义了根据jsoup ...
摘要:学习爬虫的背景了解。但是搜索引擎蜘蛛的爬行是被输入了一定的规则的,它需要遵从一些命令或文件的内容,如标注为的链接,或者是协议。不同领域不同背景的用户往往具有不同的检索目的和需求,搜索引擎无法提供针对具体某个用户的搜索结果。 学习python爬虫的背景了解。 大数据时代数据获取方式 如今,人类社会已经进入了大数据时代,数据已经成为必不可少的部分,可见数据的获取非常重要,而数据的获取的方式...
摘要:大奉打更人卖报小郎君这个人仙太过正经言归正传从红月开始黑山老鬼稳住别浪跳舞二解析数据是一个可以从或文件中提取数据的库。 目录 一、XPath解析数据 1、XPath解析数据 2、XML的树形结构 3、使用XPath选取节点 4、课堂案例 - 爬取起点小说网 二、BeautifulSoup解析...
阅读 1173·2023-01-14 11:38
阅读 1162·2023-01-14 11:04
阅读 992·2023-01-14 10:48
阅读 2546·2023-01-14 10:34
阅读 1249·2023-01-14 10:24
阅读 1132·2023-01-14 10:18
阅读 738·2023-01-14 10:09
阅读 824·2023-01-14 10:02