资讯专栏INFORMATION COLUMN

今天主要就是汇总JavaScript数组的9中不同方法汇总,也将详细示例展示给大家。
如果你还不知道数组实例中迭代方法有什么区别,可以看下面这张图: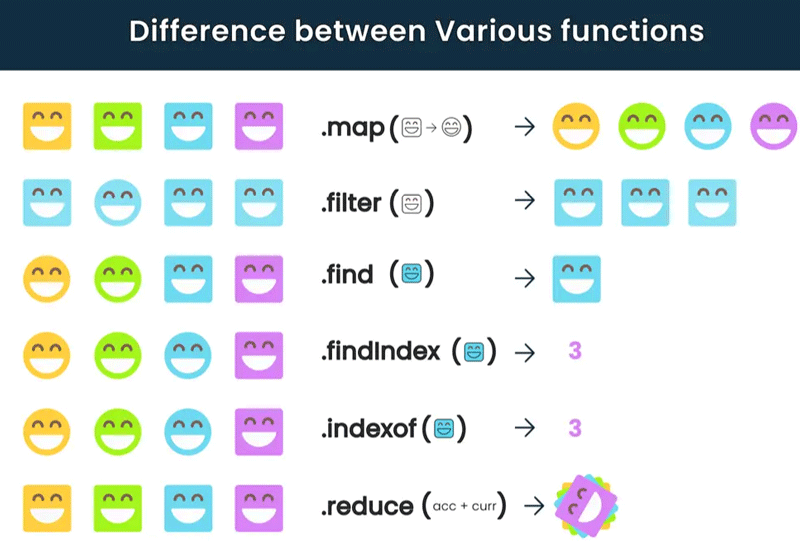
map
代表返回一个新的数组,且数组中的每一项都是执行过map提供的回调函数结果。
实现代码如下:
const map = (array, fun) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
// 定义一个空数组,用于存放修改后的数据
let res = []
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
res.push(fun(array[i]))
}
return res
}
// 测试
let res = map([1, 2, 3], item => {
return item * 2
})
console.log(res) // [ 2, 4, 6 ]
filter
这个也是返回一个新的数组,但不同的是这个数组中的值是满足filter提供的回调函数的值,
实现代码如下:
const filter = (array, fun) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
// 定义一个空数组,用于存放符合条件的数组项
let res = []
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// 将数组中的每一项都调用传入的函数,如果返回结果为true,则将结果push进数组,最后返回
fun(array[i]) && res.push(array[i])
}
return res
}
// 测试
let res = filter([1, 2, 3], item => {
return item > 2
})
console.log(res) // [ 3 ]some
这是判断数组中的每一项,当有一项满足回调函数中条件就返回true都不满足则返回false。
实现代码如下:
const some = (array, fun) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
let flag = false
for (let i of array) {
if (fun(i)) {
flag = true
break
}
}
return flag
}
let res = some([1, 2, 3], item => {
return item > 2
})
console.log(res) // trueevery
这也是判断数组中的每一项,只是它表示的是如果所有项满足回调函数中条件就返回true否则返回false。
实现代码如下:
const every = (array, fun) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
let flag = true
for (let i of array) {
if (!fun(i)) {
flag = false
break
}
}
return flag
}
let res = every([1, 2, 3], item => {
return item > 0
})
console.log(res) // truereduce
这个就是让数组中的每个元素执行我们提供的回调函数,并将结果汇总返回,实现代码如下:
const reduce = (array, fun, initialValue) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
let accumulator = initialValue
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
accumulator = fun(accumulator, array[i], i, array)
}
return accumulator
}
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(arr.reduce(v => v + 10, 10)) // 40
console.log(reduce(arr, v => v + 10, 10)) // 40forEach
这个就是遍历数组方法,数组中的每一项都执行回调函数,实现代码如下:
const forEach = (array, fun) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
for (let i of array) {
fun(i)
}
}
let res = forEach([1, 2, 3], item => {
console.log(item)
})find和findIndex
这两个方法比较类似,一个返回元素,一个返回元素的索引,这里就编写一个,实现代码如下:
const myFind = (array, fun) => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof fun !== 'function') throw new TypeError(fun + ' is not a function')
let res
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (fun(array[i])) {
res = array[i]
}
}
return res
}
// 测试
let res = myFind([1, 2, 3], item => {
return item > 2
})
console.log(res) // 3join
该方法可以将数组中的所有元素根据指定的字符串进行拼接,并返回拼接后的字符串,
实现代码如下:
const join = (array, separator = ',') => {
// 类型约束
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(array) !== '[object Array]')
throw new TypeError(array + ' is not a array')
if (typeof separator !== 'string')
throw new TypeError(separator + ' is not a string')
let res = array[0].toString()
for (let i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
res += separator + array[i + 1].toString()
}
return res
}
// 测试
let res = join([1, 2, 3], '-')
console.log(res) // 1-2-3总结
这九种数组都已示例,希望大家在运用中可以对每个都熟练掌握。
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载,若此文章存在违规行为,您可以联系管理员删除。
转载请注明本文地址:https://www.ucloud.cn/yun/127984.html
摘要:第一题为的返回值。返回值其中的每个元素均为关联的原始数组元素的回调函数返回值的新数组。修改数组对象数组对象可由回调函数修改。方法启动后的条件元素是否传递给回调函数在数组的原始长度之外添加元素。 JavaScript Puzzlers! 被称为 javascript 界的专业八级测验,感兴趣的 jser 可以去试试。 我试了一下, 36 道题只做对了 19 道, 算下来正确率为 53%,...
摘要:示例语法作用方法用于删除并返回数组的最后一个元素。返回值一个新的字符串,该字符串值包含的一个子字符串,其内容是从处到处的所有字符,其长度为减。返回值一个新的字符串,包含从的包括所指的字符处开始的个字符。 1.concat()语法:arrayObject.concat(array1,array2,......,arrayn)作用:concat() 方法用于连接两个或多个数组。特征:该方法...
摘要:函数可以没有返回值,会在最后面返回一个。事物的行为在对象中用方法来表示。 11. 函数 11.1 函数的基础知识 为什么会有函数? 在写代码的时候,有一些常用的代码需要书写很多次,如果直接复制粘贴的话,会造成大量的代码冗余;函数可以封装一段重复的javascript代码,它只需要声明一次,就可以多次调用; 冗余代码: 冗余:多余的重复或啰嗦内容 缺点: 代码重复,可阅读性差 ...
摘要:本章将介绍基本的数据结构。松鼠人一般在晚上八点到十点之间,雅克就会变身成为一只毛茸茸的松鼠,尾巴上的毛十分浓密。我们将雅克的日记表示为对象数组。 来源:ApacheCN『JavaScript 编程精解 中文第三版』翻译项目原文:Data Structures: Objects and Arrays 译者:飞龙 协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 自豪地采用谷歌翻译 部分参考了《Jav...
摘要:语法参数必填项,字符串或正则表达式,该参数指定的地方分割可选该参数指定返回的数组的最大长度,如果设置了该参数,返回的子字符串不会多于这个参数指定的数组。该数组通过在指定的边界处将字符串分割成子字符串。把正则表达式拆分成小表达式。 正则表达式是什么 RegExp 对象表示正则表达式,它是对字符串执行模式匹配的强大工具。 为什么使用正则表达式 测试字符串内的模式。例如,可以测试输入字符串...
阅读 773·2023-03-27 18:33
阅读 1005·2023-03-26 17:27
阅读 891·2023-03-26 17:14
阅读 826·2023-03-17 21:13
阅读 757·2023-03-17 08:28
阅读 2236·2023-02-27 22:32
阅读 1633·2023-02-27 22:27
阅读 2596·2023-01-20 08:28